David Jones( Woolworth Holdings Limited) – Employees’ Performance Evaluation Case Study

Introduction
Employees’ performance evaluation allows companies to effectively track analyze and evaluate their employee performance and productivity. This system should distribute forms for feedback, collect data, manage administrative tasks like sign-offs, analyze information about performance and store feedback securely. In this paper, David Jones is chosen to show the performance review system and the feedback process for managers.
1. A brief overview of David Jones
3David Jones is a subsidiary of parent organization Woolworths Holdings Limited. David Jones is a retail upmarket department store and it was founded in the year 1838. However, in the year 1980, Adelaide Steamship Company completed the acquisition and during the 1990s the assets of the company floated as David Jones Limited for the recession. After 2000, David Jones has been into the turbulent times and it did the merger with Myer and in the year 2014, Woolworths took over the company. In the year 2016, Woolworths sold the Market Street store and the company announced the relocation of the office of DJ in Melbourne (Davidjones.com 2018). David Jones sells products like cosmetics, fashion, furniture, home appliances, electrical and food.
In the year 2016, the revenue of the organization touched AU$ 2.2 billion and the operating income of the organization was AU$ 170 million. At present, David Jones has the employees of 8100 and the maximum of the employees are directly employed by the HR department (Davidjones.com 2018). David Jones has 45 stores in Australia; most of them are located in Australian territories and states, except Northern Territory and Tasmania. David Jones faces its competition mainly from Myer and David Jones opened its first New Zealand store in Wellington in the year 2016 buying Kirtkcaldie and Stains.
2. A description of the stages in the Employee Performance Review process
According to Dall’ Ora et al. (2016), an effective employee performance process helps the managers to measure and evaluate individual performance of the employees and to optimize the productivity of the employees. The employee performance review aligns strategic business objectives with the employee’s day-to-day actions in order to support the career planning, remuneration, and compensation.
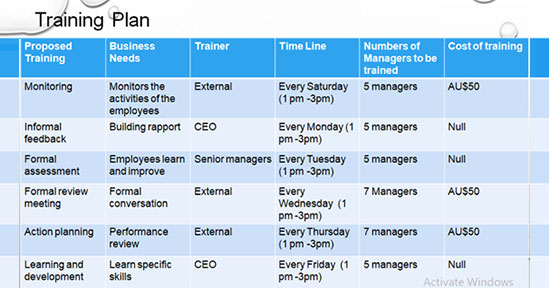
The Employee Performance Review Process has six stages and it starts with Monitoring. The management monitors the activities of the employees including the performance, job satisfaction and motivation. Monitoring process tracks the employee motivation through observation of the employees’ enthusiasm. The management also calculates the responses of the employees to determine the performance of the employees. Monitoring of the employees can be done in three different ways; technical monitoring, financial monitoring and process monitoring of the employees.
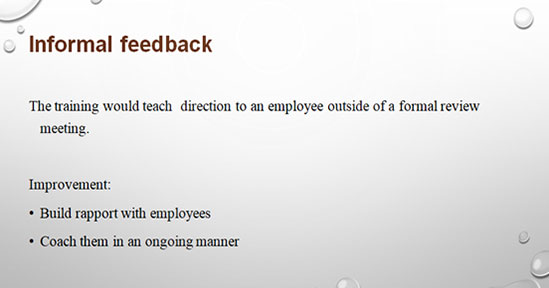
The second stage is informal feedback and in this stage, the manager provides important feedback along with direction to the employees outside of the roundtable meeting. Informal feedback is very significant for the employees as it helps to build rapport with the managers and to take the coaching from the manager as well (Anitha 2014). Informal feedback can be taken during the office hours and the employees can improve the performance real-time through informal feedback.
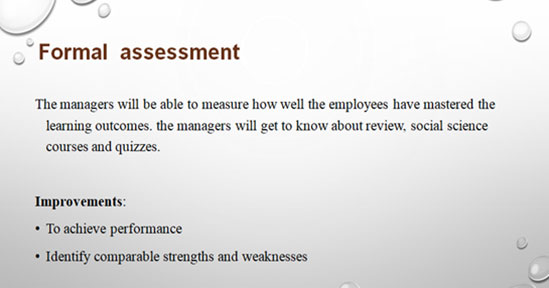
The third stage is about formal assessment and in this stage; the managers take the test and systematically measure how much the employees learn and improve. According to Nielsen et al. (2017), formal assessments are standardised, used and scored to compare the employees. Formal assessments are usually the assessments which are used to determine the employees’ grade and performance. Examples of formal assessments are assignments, projects and quizzes.
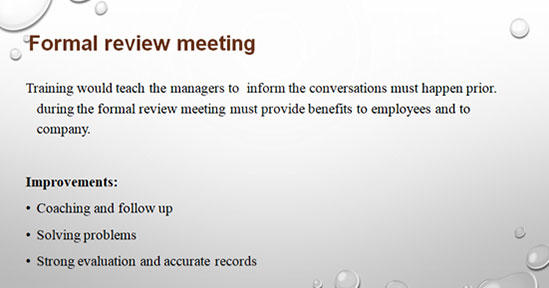
The formal review meeting is the fourth stage in which the employees have to meet the managers for the formal conversation based on the informal feedback that has occurred prior. The objective of the formal review meeting is to make the overall face-to-face encounter productive which can produce benefits for both the company and the employees.
The fifth stage is action-planning and the managers and supervisors make an action plan for the employees through discussions. Employees’ regular performance review shows significant room for improvement and performance action-plan helps the employees to get back on the track. This action plan is the constructive discussion between the managers and the employers.
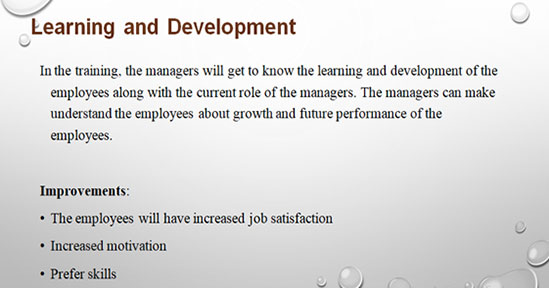
The sixth stage is learning and development and the managers facilitate the employees to take the training programme in which sections the employees lack. Training programmes help the employees to learn specific skills and knowledge to develop the performance in the current roles (Timmers et al. 2015). Performance review process helps the employees to develop skills and focuses the employees for future performance and growth.
3. A memo from the Human Resource Manager to all employees outlining the Employee Performance Review process
To: The employees
CC: The CEO
From: The Human Resource Manager
Date: 12/10/2018
Subject: Outlining the Employee Performance Review Process
This is to inform that HR department of David Jones is going to remodel the Employee Performance Review Process.
David Jones declares the new Employee Performance Review Process and this review process has four stages.
The first step of Employee Performance Review Process is to set the performance expectations, the managers and the employees of David Jones do work together to create the clear expectation for job performance. The employees will be responsible for accomplishing the objectives and managers will provide guidance.
The second step is about obtaining and providing the guidance. In David Jones, giving and getting is a critical part of controlling the employees. The managers will provide constructive feedback to the employees on changing behaviour. The employees will open to receive constructive feedback to improve the behaviour. The managers will be using praise, coaching and document performance progress notes to provide guidance.
The third stage is the annual performance review meeting and David Jones sets the collaborative process which is mainly competency based and it is focusing on the development of the employees. Employees need to complete the self-review form before scheduling the meetings with the managers. The primary purpose of this stage is to develop and enhance skills of David Jones employees at all levels.
The fourth stage is creating a plan for the employees and each of the employees must have the Individual Development Plan. In addition, it is the employees’ responsibility to create the plan and to share it with the senior managers.
Whole-Hearted cooperation is highly solicited.
4. An instruction training PowerPoint slide pack to train managers in the Employee Performance Management process
5. A Sample Employee Performance Review form
| Employee Information | |||
| Employee Name | Department | ||
| Employee ID | Reviewer Name | ||
| Position Held | Reviewer Title | ||
| Last Review Date | Today’s Date | ||
| Characteristics | |||
| Quality | Unsatisfactory | Good | Excellent |
| Quality to full potential | |||
| Quality of work | |||
| Work consistency | |||
| Communication | |||
| Independent work | |||
| Take initiative | |||
| Productivity | |||
| Creativity | |||
| Integrity | |||
| Co-worker relation | |||
| Technical skills | |||
| Punctuality | |||
| Attendance | |||
| Goals | |||
| Achieved Goals set in the Previous Review? | |||
| Goals for the next review period? | |||
| Comments and Approval | |||
| Comments | |||
6. A guide for managers in providing feedback at the Employee Performance Review meeting
During the performance review meeting, the role of the managers is very important to assess the degree to which the employees can attain agreed-upon goals. In David Jones, the managers provide valuable feedback to the employees.
Tell and Sell: In Tell and Sell feedback, the managers of David Jones must assume the aim of providing the performance judgement to the employees, obtaining their acceptance. The objective of telling and sell method of feedback is to tell the employees about their performance, acceptance and gain of the evaluation so that the employees can persuade to follow their plan of improvement (Wang et al. 2015). Role of the managers would be sentencing the judge and attitude of the managers would be that the employees must appreciate the advice. Managers of David Jones provide positive feedback to the report of Employee Performance Review. The positive feedback of the managers is generally motivating to the employees. Tell-and-sell feedback helps the managers of David Jones to communicate correctly to the employees and the employees will get to know where they stand.
Tell and Listen: The goal of the tell-and-listen feedback is to communicate the evaluation of the employees and the managers wait for the employees’ responses (Heller 2017). In this feedback, the managers of David Jones should play the role of attentive judge and the attitude of the managers will be based on feelings of the employees and the managers must understand the employees and respect their concern. The supervisors in David Jones tell their perception of the employees’ weaknesses and strengths. Giving a performance review to the under-performance employee is challenging for the managers as the managers may face challenges to overcome the discomfort (Bersin 2015). The managers during the meeting can ask the employees to complete self-assessment and it is the easy way to observe how the employees perceive their own work. The managers listen to the feeling of the employees and the managers cannot refute the employees’ objections. The managers must consider both the views to reach conclusion and plan for the development.
Problem-solving: In problem-solving feedback, the aim is to discuss assessment jointly and encourage the employees to improve and develop. Roe of the managers in David Jones will be to play the role of a coach and attitude of the managers would be the mutual and constructive approach to find the best to correct the problems. The problem-solving feedback is effective when it is objective, specific, structured and not graded and allows for the identification of weaknesses and strengths. The managers mostly do the mistake of giving constructive feedback to the underperformers; not to the top performers as top performers of the organisation also need constructive feedback (Fong et al. 20176). The managers in David Jones should take time before providing constructive feedback so that they can provide solutions to problems. The managers need to deliver feedback using the growth mindset. In David Jones, the managers find the solution together with the employees during the constructive feedback.
Conclusion
It has been noted that the performance evaluation system of David Jones can dramatically streamline existing performance management strategies. This can result in substantial time savings for managers, employees and HR. It also can be an opportunity for companies to increase the amount of feedback data they collect on employees. Performance evaluation and remuneration from the management should be maintained with strategies in David Jones.
Reference List
Ishizaka, A. and Pereira, V.E., 2016. Portraying an employee performance management system based on multi-criteria decision analysis and visual techniques. International Journal of Manpower, 37(4), pp.628-659.
Timmers, C.F., Walraven, A. and Veldkamp, B.P., 2015. The effect of regulation feedback in a computer-based formative assessment on information problem-solving. Computers & Education, 87, pp.1-9.
Anitha, J., 2014. Determinants of employee engagement and their impact on employee performance. International journal of productivity and performance management, 63(3), p.308.
Dall’Ora, C., Ball, J., Recio-Saucedo, A. and Griffiths, P., 2016. Characteristics of shift work and their impact on employee performance and wellbeing: A literature review. International journal of nursing studies, 57, pp.12-27.
Nielsen, K., Nielsen, M.B., Ogbonnaya, C., Känsälä, M., Saari, E. and Isaksson, K., 2017. Workplace resources to improve both employee well-being and performance: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Work & Stress, 31(2), pp.101-120.
Wang, M., Burlacu, G., Truxillo, D., James, K. and Yao, X., 2015. Age differences in feedback reactions: The roles of employee feedback orientation on social awareness and utility. Journal of Applied Psychology, 100(4), p.1296.
Bersin, J., 2015. Becoming irresistible: A new model for employee engagement. Deloitte Review, 16(2), pp.146-163.
Heller, M., 2017. Real-time, ongoing employee feedback: the perk that actually retains. Strategic HR Review, 16(3), pp.125-130.
Fong, C.J., Warner, J.R., Williams, K.M., Schallert, D.L., Chen, L.H., Williamson, Z.H. and Lin, S., 2016. Deconstructing constructive criticism: The nature of academic emotions associated with constructive, positive, and negative feedback. Learning and Individual Differences, 49, pp.393-399.
David Jones. 2018. Retail Australia. https://www.davidjones.com/ [Accessed 12th Oct 2018]